Stars Milky Way
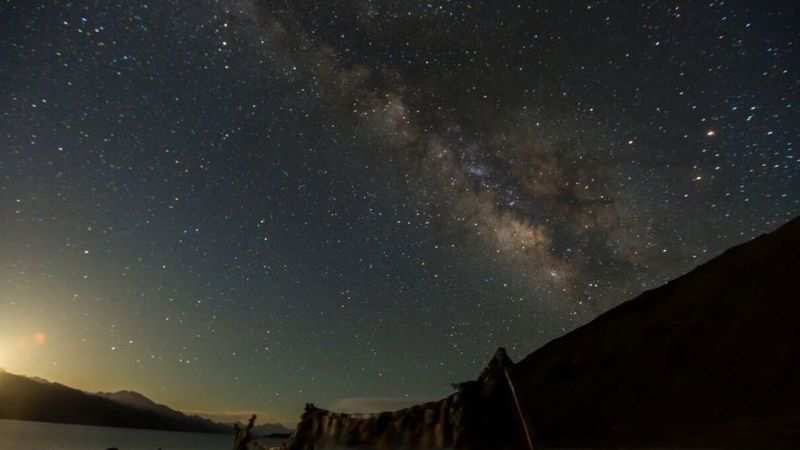
All the stars we see in the night sky are in our own milky way galaxy.
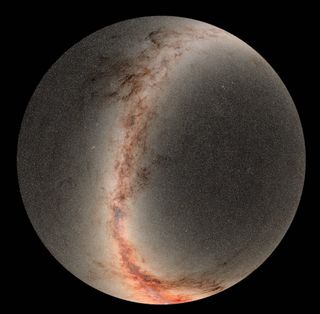
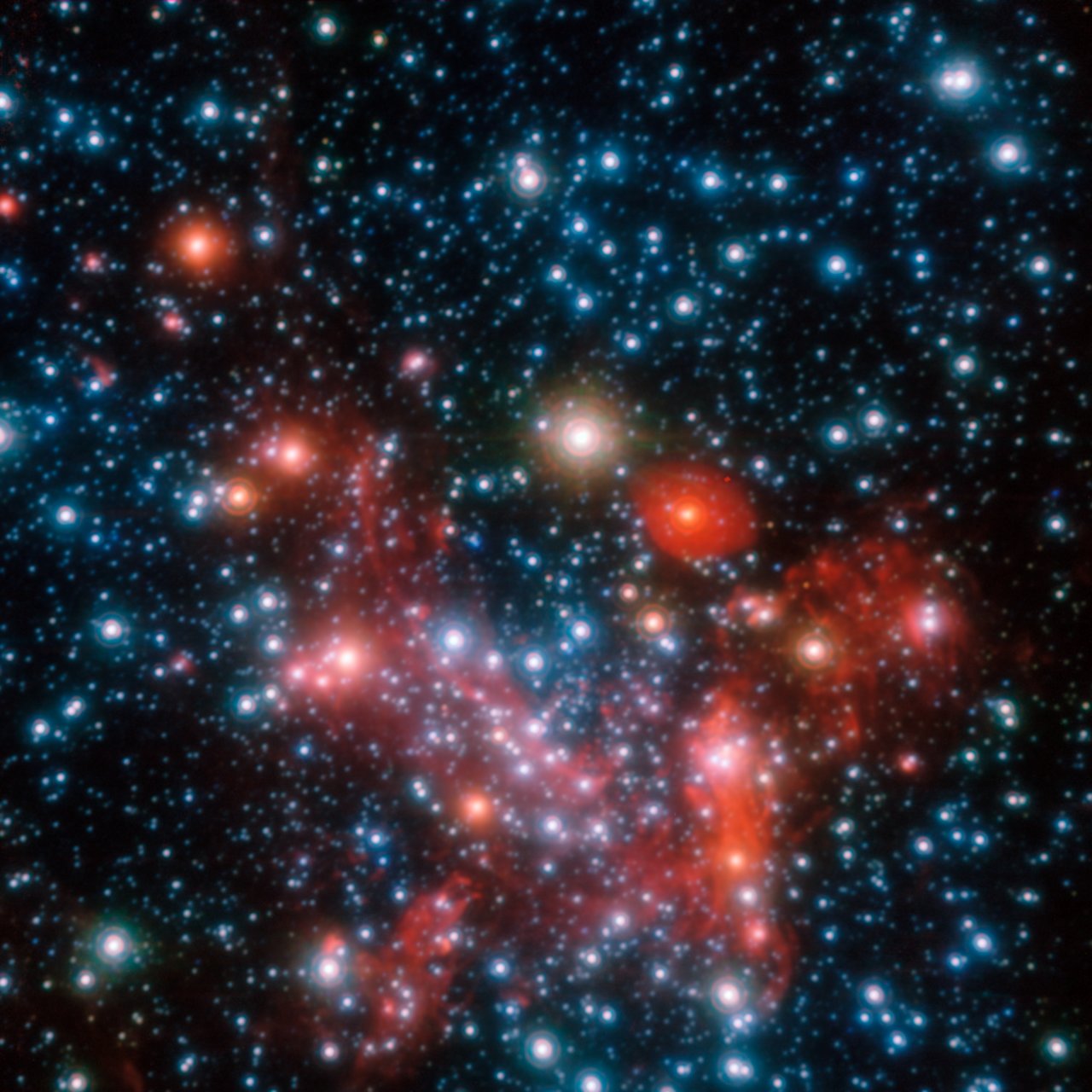
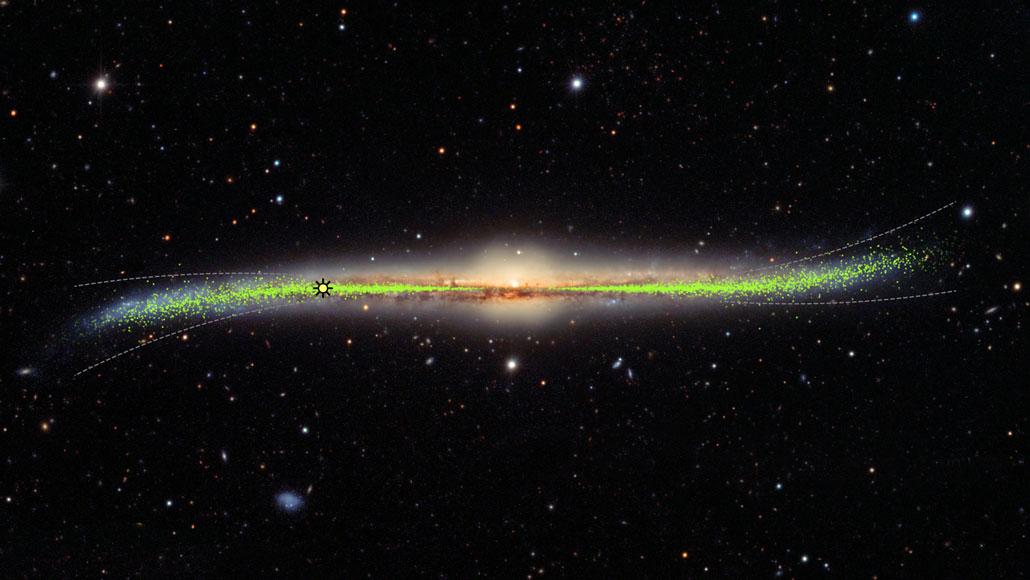
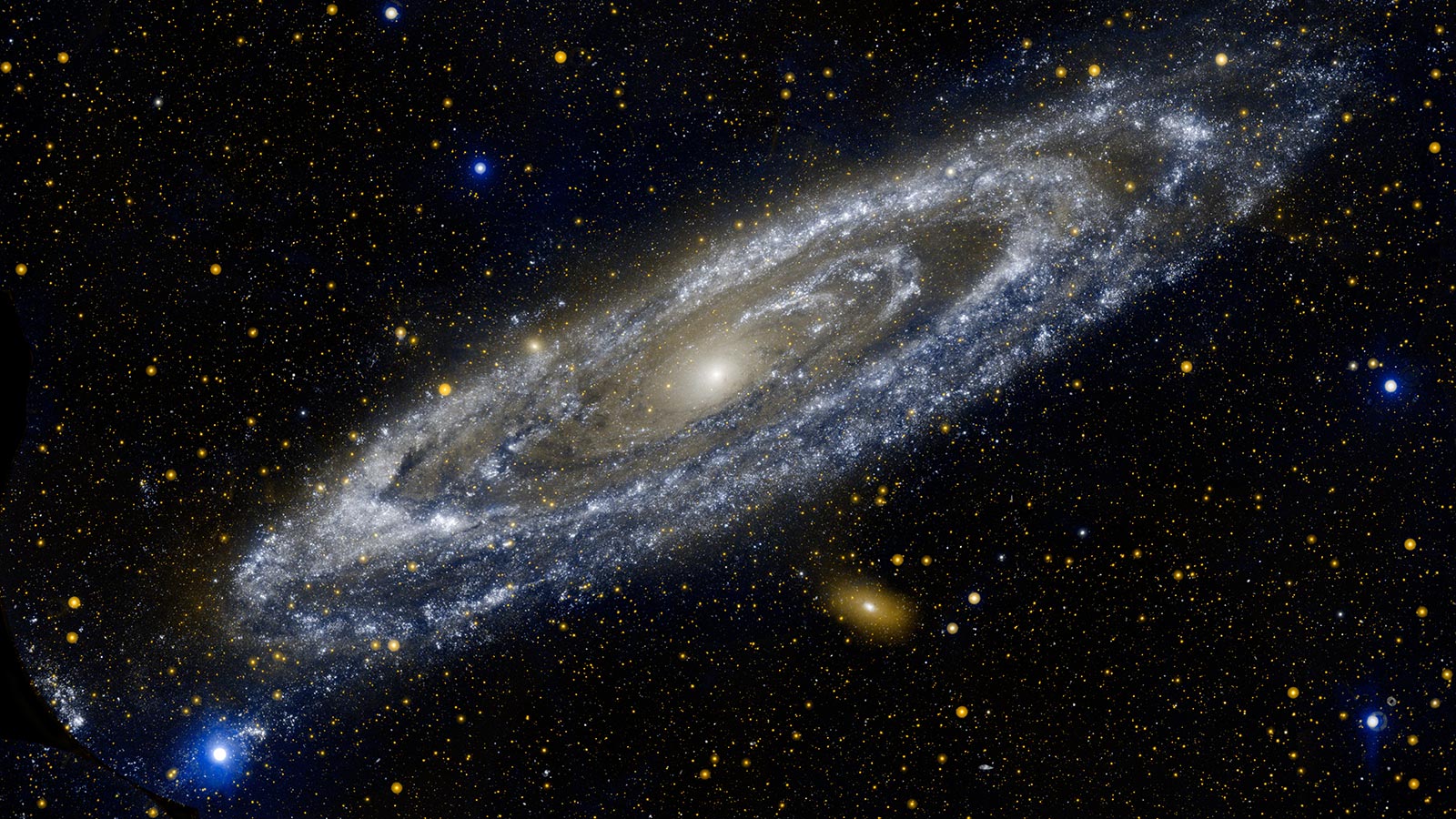
Stars milky way. The oldest stars in the milky way are nearly as old as the universe itself and thus probably formed shortly after the dark ages of the big bang. A galaxy is a large group of stars gas and dust bound together by gravity. An illustration based on data form the gaia spacecraft shows the distribution of 150 million stars in the milky way with orange and yellow hues highlighting greater stellar densities. The stars in the milky way have similar chemical makeups because they emerged from the same clouds of gas infused over time with a range of elements from the stellar explosions we call supernovae.
There are different models for estimating the number of stars in the milky way and the answers they give differ depending on what is used as the average mass of a star. They come in a variety of shapes and sizes. In one calculation the milky way has a mass of about 100 billion solar masses so it is easiest to translate that to 100 billion stars. The most common answer seems to be that there are 100 billion stars in the milky way on the low end and 400 billion on the high end.
This accounts for the stars that would be bigger or smaller.











/arc-anglerfish-arc2-prod-bonnier.s3.amazonaws.com/public/TBQV2YXFSL7EXOJZBO4RG5I6D4.png)




:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16002803/milky_way_pie.jpg)





